Presented By: Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
EEB Thursday Seminar: Counter-intuitive ecological dynamics: subsystem instability as a driving mechanism
Michael Cortez, Mathematics and Statistics, Utah State University
Abstract
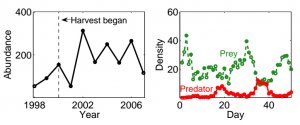
Intuition suggests that increasing species mortality (e.g, through harvesting) will cause a decrease in population abundance. Yet, in some systems, increased mortality causes an increase in abundance (panel A); this is known as a hydra effect. Classical ecological theory predicts that in predator-prey cycles, peaks in prey density are followed by peaks in predator density. However, cycles exhibiting different patterns (even the reverse!) have been observed in many empirical system (panel B). In this talk, I show that the underlying mechanism connecting and driving these unexpected and counter-intuitive patterns is subsystem instability, i.e., instability in a subcommunity of the whole community is responsible for altering population and community-level ecological dynamics. For predator-prey systems, I show that both patterns are driven by instability in the prey subcommunity (caused by either interspecific or intraspecific prey variation). I then discuss how these results extend to communities of any size. Together, this work suggests subsystem instability may be an important general mechanism driving population and community-level dynamics in natural systems.
Light refreshments served at 4 p.m.
Intuition suggests that increasing species mortality (e.g, through harvesting) will cause a decrease in population abundance. Yet, in some systems, increased mortality causes an increase in abundance (panel A); this is known as a hydra effect. Classical ecological theory predicts that in predator-prey cycles, peaks in prey density are followed by peaks in predator density. However, cycles exhibiting different patterns (even the reverse!) have been observed in many empirical system (panel B). In this talk, I show that the underlying mechanism connecting and driving these unexpected and counter-intuitive patterns is subsystem instability, i.e., instability in a subcommunity of the whole community is responsible for altering population and community-level ecological dynamics. For predator-prey systems, I show that both patterns are driven by instability in the prey subcommunity (caused by either interspecific or intraspecific prey variation). I then discuss how these results extend to communities of any size. Together, this work suggests subsystem instability may be an important general mechanism driving population and community-level dynamics in natural systems.
Light refreshments served at 4 p.m.
Explore Similar Events
-
Loading Similar Events...
